Congratulations!
You have successfully registered for the training. Our team of specialists will be in touch with you shortly.
Go back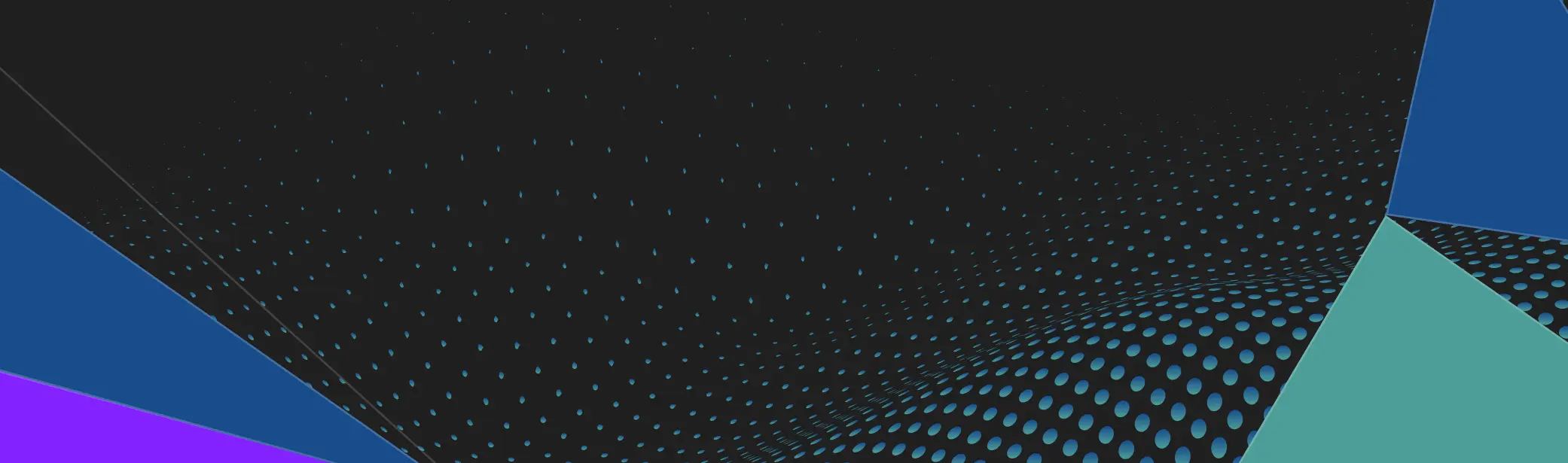

 Georgia
Georgia
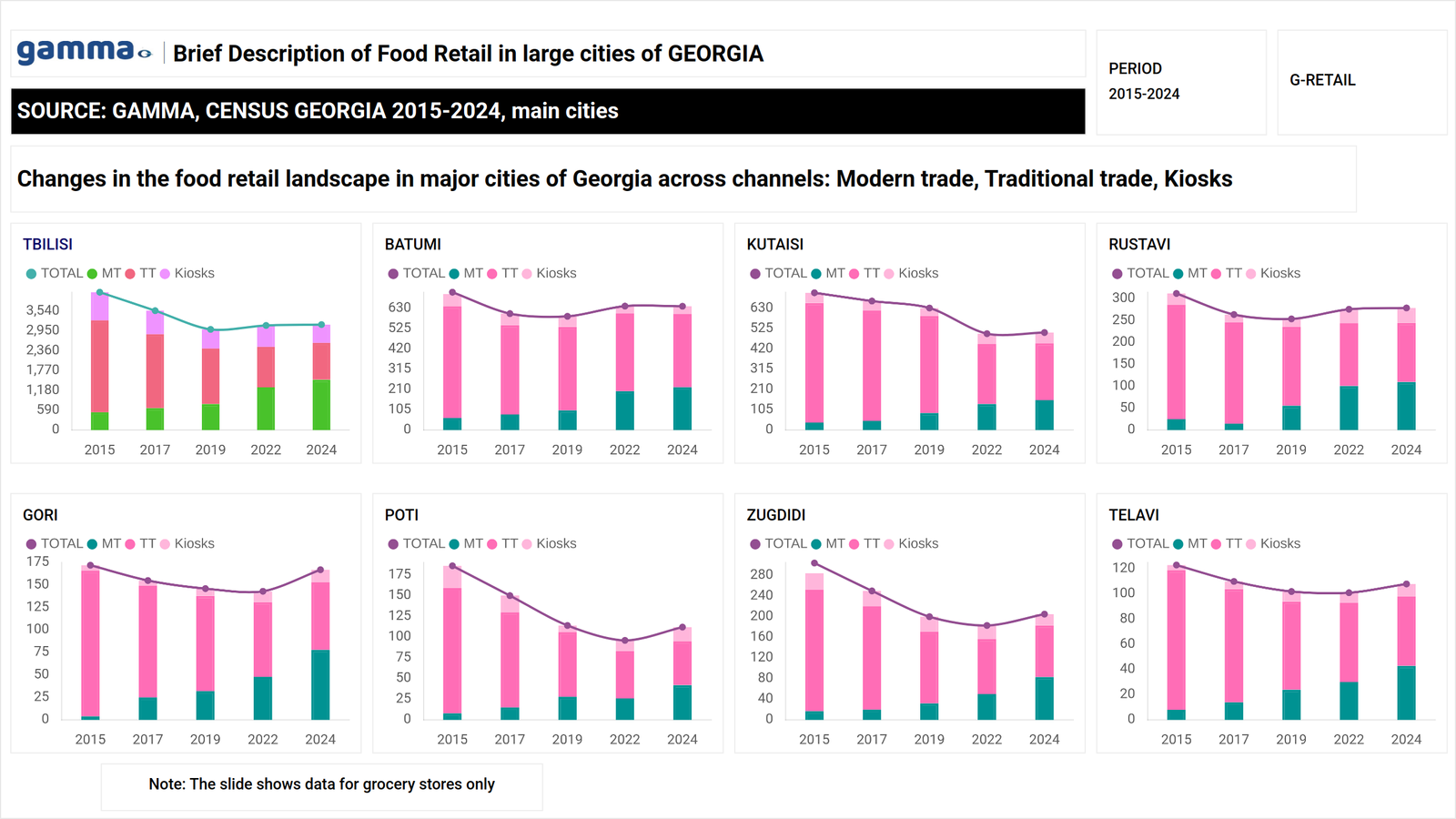
The analysis is based on a retail Census regularly conducted by GAMMA Research. In Georgia, the Census covers Tbilisi and seven major cities and is designed to map the entire actual retail infrastructure. In addition to infrastructure mapping, the analysis incorporates consumer behavior data from GAMMA’s BESIDE project, enabling the interpretation of retail structure through the lens of shopper missions and behavioral patterns.
In urban areas, grocery retail in the surveyed cities has moved beyond the phase of extensive growth and entered a stage of structural saturation. Quantitatively, the increase in the number of retail outlets remains limited (approximately +2.5% in 2024 vs. 2022), signaling a slowdown in expansion and intensifying competition within the existing infrastructure.
The current phase of market development is characterised by:
-High retail outlet density
-Significant overlap of catchment areas
-Competition for the same pedestrian and transport flows
Stores are increasingly located according to an “umbrella principle,” whereby multiple outlets of different formats operate within short walking distance of each other. As a result, store choice is driven less by proximity and more by the specific shopping mission at a given moment.
Modern Trade: Quantitative Growth Without Hypermarketisation
From an international perspective, Georgia’s Modern Trade model appears atypical. While the channel has expanded quantitatively – recording an increase of around 20% in store numbers across cities – the nature of this growth differs from classic retail development patterns.
Modern Trade growth in Georgia:
-Is not driven by hypermarket expansion
-Does not rely on large shopping centers
-Does not alter the underlying behavioral logic of the market
In the Georgian context, Modern Trade primarily consists of minimarkets, compact self-service formats, and limited but high-turnover assortments. Market modernisation, therefore, reflects the standardisation of neighborhood retail rather than a transition toward large-scale formats.
Traditional Trade: Adaptation and Format Convergence
Traditional Trade remains structurally important, particularly in residential areas and regional cities. Compared to 2022, the channel declined by approximately 8%, reflecting a gradual redistribution of roles within the retail landscape.
The resilience of Traditional Trade is driven by:
-Maximum proximity to consumers
-Strong habit formation and trust
-Flexibility in assortment and pricing
At the same time, the channel is undergoing adaptation: the share of self-service elements is increasing, visual standards are improving, and functionally, Traditional Trade is converging with minimarket formats. The market is not moving toward the disappearance of Traditional Trade, but toward a progressive blurring of boundaries between Modern and Traditional formats.
Kiosks: From Sales Point to Drive Point
One of the most visible structural shifts in 2024 has been the transformation of kiosks. Quantitatively, the channel declined by approximately 10% compared to 2022, yet its functional role has strengthened.
Following the ban on open cigarette displays, kiosks lost their primary visual driver and were forced to rethink their operating model. This led to a reorientation toward:
-Coffee-to-go
-“Window + fast service” formats
-Beverages and immediate consumption
Today, kiosks increasingly function as “drive points” that compete not so much with other stores as with the consumer’s time.
Structural saturation is evident both in the number of retail outlets and in the volume of physical retail space. The total retail space of Food & Mix formats exceeds 520,000 square meters, while the average availability ratio stands at 3.6 stores per 1,000 inhabitants – one of the highest levels in the region.
This combination indicates double saturation: by outlet count and by retail space. Under such conditions, further expansion of retail space does not generate new demand, but instead redistributes existing consumer traffic among stores within the same walkable area. Excess retail space reinforces the “umbrella principle” and drives fragmented purchasing: loyalty shifts from individual stores to the convenience of the route.
From Basket to Route: How Urban Shopping Works Today
Georgia’s urban retail market has shifted toward a model characterised by high purchase frequency and small basket size. Growth is driven not by increases in average basket value, but by the repeatability of consumer contacts throughout the day.
Shopping is no longer a single destination, but a route. Consumers distribute their purchases across multiple locations, selecting formats based on specific missions (e.g. quick top-up vs. planned needs).
Despite growing digital engagement, the final decision-making process remains firmly offline. Physical availability and convenience ultimately determine the purchase.
Market Development Trajectory
Georgia’s food retail market is evolving gradually without abrupt structural disruptions. Key directions include:
-Continued strengthening of small, structured formats
-Growing functional importance of kiosks
-Increasing dominance of mission-driven shopping
-Lack of prerequisites for large-scale hypermarket expansion.
In 2025, Georgia’s retail market is in a phase of structural maturity. With 3.6 Food & Mix stores per 1,000 inhabitants and over 520,000 square meters of space, the market is saturated, limiting opportunities for extensive growth.
Success now depends on the redistribution of existing traffic. Price and integration into the consumer’s daily route have replaced “space and assortment” as critical success factors. As Traditional Trade converges with Modern formats and kiosks transform into service-heavy “drive points,” the market has become a highly competitive, offline-centric ecosystem where victory goes to those most precisely embedded in daily consumer habits.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
GAMMA Research would be glad to collaborate in the future with brands and retailers interested in better understanding retail dynamics and consumer behavior.

 Georgia
Georgia
This overview combines GAMMA Census 2023, providing a comprehensive view of the Drogerie channel’s retail structure and geographic presence in Georgia
Read more

 Georgia
Georgia
This analytical review is based on a combination of quantitative and qualitative research conducted by GAMMA Research between 2019 and 2025.
Read more

 Armenia
Armenia
Our company has completed a census of the retail network in three major cities of Armenia: Yerevan, Gyumri, and Vanadzor. The results of the census revealed significant changes in the retail landscape of the country over the past nine years.
Read more
You have successfully registered for the training. Our team of specialists will be in touch with you shortly.
Go back